The importance of frequency management in HF radio communication
The importance of frequency management in HF radio communication
Explore how frequency management in HF radio boosts communication reliability, reduces interference and enhances long-distance performance.
HF communications serve indispensable functions across industries such as aviation, maritime and remote operations. However, radio waves in the HF band encounter impediments to transmission like signal attenuation and interference — notably when conditions are unstable. To counteract these hurdles and ensure clear, dependable connections over long distances demands sophisticated frequency administration.
Analysis of link quality and channel performance
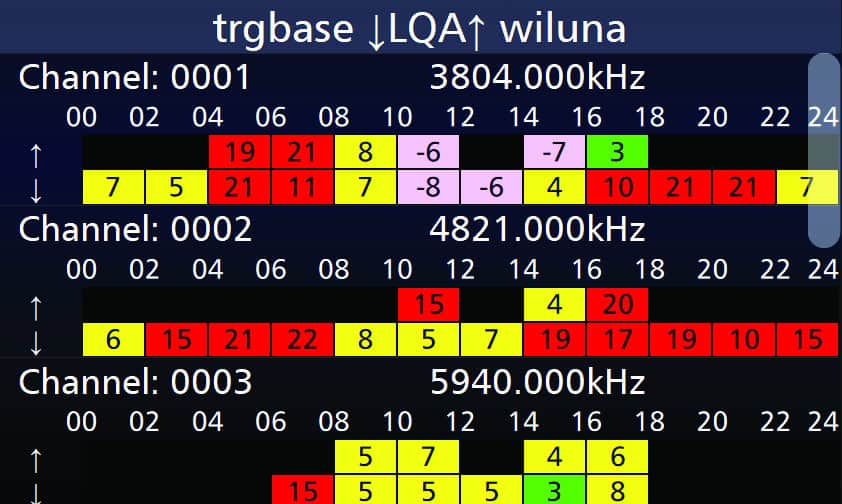
HF radio systems rely on link quality analysis (LQA) to adapt to changing channel conditions. LQA compiles data from previous transmissions, analyzing metrics such as multipath fading, signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and bit error rate (BER). This information is used to construct a ranked frequency matrix, which identifies the most reliable channels for communication.
By evaluating factors like SINAD (signal-to-noise-and-
Automatic link establishment and channel switching
One important component of HF systems is automatic link establishment (ALE), which uses an LQA matrix to routinely scan for and select trustworthy frequencies. ALE ensures connectivity with minimal disruption by automatically building communication relationships.
A handshake protocol measures the signal to noise ratio (SNR) of a frequency and updates this reading in the LQA table upon every interaction. When the SNR of a particular frequency begins to decline, the ALE protocols will automatically change to a “better” frequency based on the updated results.
For long-distance operations in environments where signal strength can fluctuate due to atmospheric changes, solar activity, or interference, ALE’s ability to adjust frequencies based on historical performance data is crucial for maintaining reliable communication.
Best practices in frequency assignment and spectrum monitoring
To keep HF communication steady, it is essential to assign frequencies effectively and monitor the spectrum. Network performance and interference can be optimised by following best practices.
- Frequency assignment: Lower frequencies (3-10 MHz) are ideal for long-range communication, especially at night when propagation conditions improve. Higher frequencies (10-30 MHz) perform better over shorter distances and during the day.
- Spectrum monitoring: Continuous monitoring identifies interference from sources like other radio systems or solar flares.
HF systems benefit from frequency selection based on spectrum monitoring and LQA insights, which improves communication reliability and efficiency. Proactive frequency planning is vital for handling changing conditions and reducing interference.
Conclusion
Certain industries, such as aviation and emergency response, rely heavily on HF radio communication, making frequency management an absolute necessity for dependable and high-quality transmissions. Tools such as automatic link establishment, link quality analysis, and frequency planning collaborate to adapt to environmental conditions, guaranteeing reliable, clear connections across extended distances. These solutions enhance system resilience by selecting frequencies based on proven reliability, hence preventing disturbances. The implementation of improved frequency management is crucial for an HF communication network to be dependable and responsive.
Contact us to learn how our solutions can strengthen your network’s performance.